Choosing the right heat pump for your home can be a daunting task, especially with the numerous options available. Two popular types of heat pumps are air source and ground source heat pumps. Understanding the differences between them is crucial for making an informed decision.
A heat pump comparison can help you determine which type is best suited for your needs. While both types offer efficient heating and cooling, they operate in distinct ways.
By examining the characteristics of air source heat pumps and ground source heat pumps, you can decide which one aligns with your home’s specific requirements and your budget.
Key Takeaways
- Efficient heating and cooling solutions are available through both air and ground source heat pumps.
- The choice between air and ground source heat pumps depends on your home’s specific needs.
- A comparison of the two types can help you make an informed decision.
- Understanding the operating differences is crucial for selecting the right heat pump.
- Both types offer unique benefits and drawbacks.
Understanding Heat Pump Technology
At its core, heat pump technology is about harnessing and transferring heat, rather than generating it through electrical resistance. This fundamental principle allows heat pumps to provide both heating and cooling, making them a versatile solution for home climate control.
How Heat Pumps Work
Heat pumps work by transferring heat from one location to another. During the heating season, they extract heat from the outside air (or ground, in the case of ground source heat pumps) and transfer it inside the home. In the cooling season, this process is reversed, and heat is transferred from the home to the outside. This is achieved through a cycle involving a refrigerant that absorbs and releases heat.
The key components involved in this process include the compressor, condenser coil, expansion valve, and evaporator coil. Each plays a crucial role in the heat transfer process, enabling the heat pump to efficiently heat or cool a home.
The Evolution of Heat Pump Technology
Heat pump technology has undergone significant advancements since its inception. Early models were often inefficient and limited in their application. However, modern heat pumps have evolved to be more efficient, environmentally friendly, and capable of operating effectively even in colder climates.
- Improved compressor technology has enhanced efficiency and reliability.
- Advances in refrigerant technology have reduced environmental impact.
- Better system designs have improved performance in extreme temperatures.
These advancements have positioned heat pumps as a viable alternative to traditional heating and cooling systems, offering homeowners a potentially more efficient and sustainable solution.
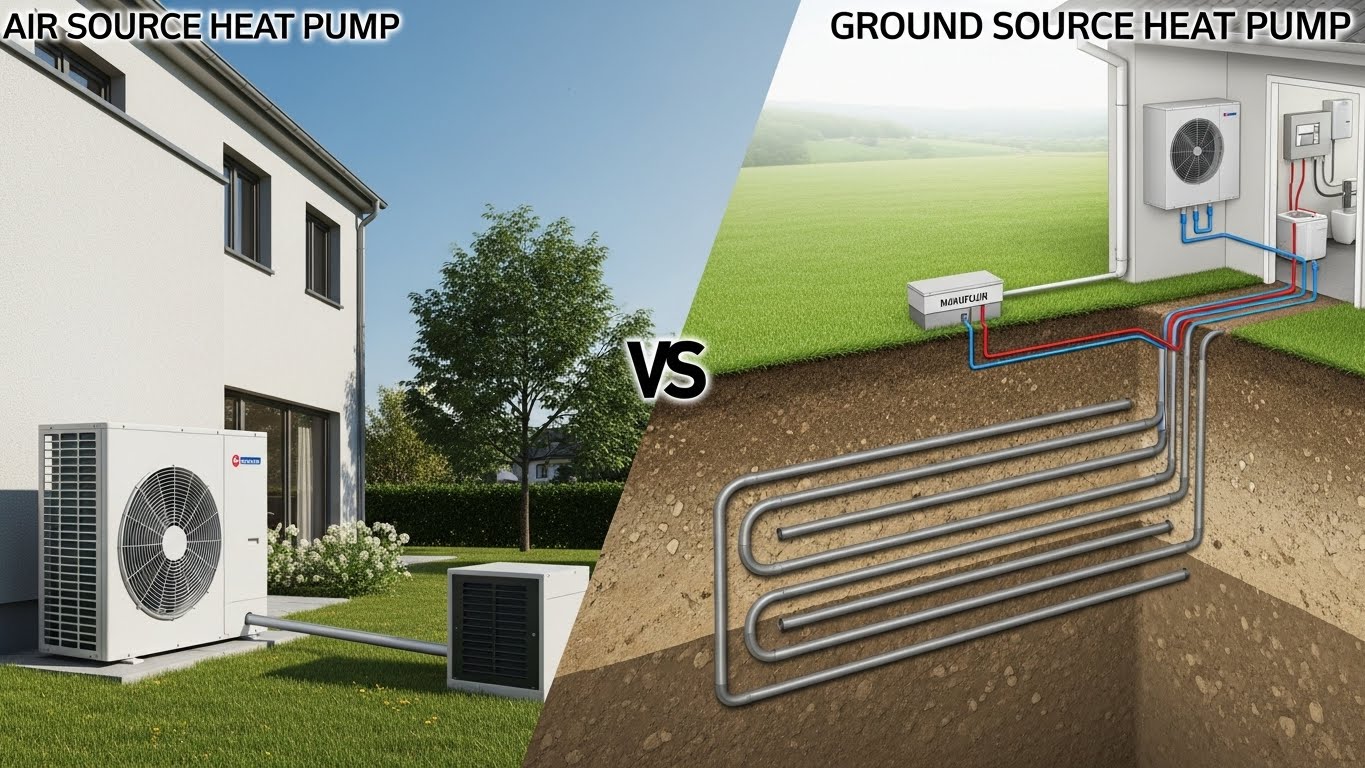
What Is an Air Source Heat Pump?
The concept of air source heat pumps is simple yet effective, utilizing outdoor air to provide warmth or cooling. Essentially, an air source heat pump is a device that transfers heat from one location to another, typically from outside a building to the inside, or vice versa, depending on the season.
Types of Air Source Heat Pumps
There are primarily two types of air source heat pumps: split systems and monoblock systems. Split systems consist of an outdoor unit and an indoor unit, making them versatile for various installation scenarios. Monoblock systems, on the other hand, house all components in a single outdoor unit, simplifying the installation process.
Key Components and Operation
The operation of an air source heat pump involves several key components: the compressor, condenser coil, expansion valve, and evaporator coil. These components work together to absorb heat from the outside air and transfer it inside, or vice versa, depending on the heating or cooling mode.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Compressor | Compresses refrigerant, raising its temperature |
| Condenser Coil | Releases heat to the outside air |
| Expansion Valve | Reduces pressure of the refrigerant |
| Evaporator Coil | Absorbs heat from the outside air |
Popular Models in the US Market
Some of the popular air source heat pump models in the US market include the Carrier Infinity Series and the Lennox XP25. These models are known for their high efficiency and advanced features such as smart technology integration and high SEER ratings.
What Is a Ground Source Heat Pump?
Unlike traditional heating systems, ground source heat pumps utilize the earth’s natural temperature to provide efficient heating and cooling for homes. This innovative technology leverages the stable temperature of the earth, typically between 50°F and 60°F, to regulate indoor temperatures.
Types of Ground Source Heat Pumps
Ground source heat pumps are categorized mainly into two types based on their installation: horizontal and vertical systems. Horizontal systems involve laying pipes in trenches, typically 4 to 6 feet deep, and are suitable for larger properties. Vertical systems, on the other hand, involve drilling boreholes, usually 150 to 300 feet deep, making them ideal for smaller or more constrained spaces.
Key Components and Operation
The key components of a ground source heat pump include the ground loop, the heat pump unit, and the distribution system. The ground loop, filled with a heat transfer fluid, absorbs or dissipates heat from the earth. The heat pump unit then transfers this heat to the home via the distribution system, which can be air, water, or a combination of both.
Leading Systems Available in America
In the US market, several leading manufacturers offer high-quality ground source heat pump systems. Brands like WaterFurnace and Nordic are renowned for their efficiency and reliability. These systems are designed to meet various home sizes and heating needs, ensuring there’s a suitable option for different homeowners.
By understanding the types, components, and operation of ground source heat pumps, homeowners can make informed decisions about adopting this energy-efficient technology.
Air Source Heat Pump vs Ground Source Heat Pump: Core Differences
The primary differences between air source and ground source heat pumps lie in their technology, operating principles, and energy sources. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for homeowners and businesses looking to invest in an efficient heating solution.
Technology Comparison
Air source heat pumps use outdoor air to provide heating, while ground source heat pumps utilize the earth’s natural temperature. Air source heat pumps are generally simpler in design and less expensive to install, whereas ground source heat pumps are more complex and require underground piping.
Operating Principles
The operating principles of these heat pumps differ significantly. Air source heat pumps extract heat from the air, even in cold temperatures, and transfer it indoors. Ground source heat pumps, on the other hand, leverage the stable temperature of the earth to provide consistent heating.
Energy Source Variations
The energy source is another key differentiator. Air source heat pumps rely on ambient air, which can be affected by weather conditions. In contrast, ground source heat pumps tap into the earth’s energy, providing a more stable and reliable source of heat.
In conclusion, the choice between air source and ground source heat pumps depends on various factors, including installation costs, operating efficiency, and environmental considerations. By understanding the core differences between these two technologies, individuals can make informed decisions about their heating needs.
Installation Requirements and Process
The installation of air source and ground source heat pumps involves distinct processes and requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial for homeowners to make informed decisions about their heating and cooling solutions.
Air Source Heat Pump Installation
Air source heat pump installation is generally less complex compared to ground source systems. It requires an outdoor unit and an indoor unit, with the outdoor unit needing to be placed in a location that allows for good airflow. The installation process typically involves assessing the home’s heating and cooling needs, selecting a suitable location for the outdoor unit, and ensuring that the indoor unit is properly connected to the home’s ductwork or configured for ductless operation.
Ground Source Heat Pump Installation
Ground source heat pump installation is more involved due to the need for underground piping. This process includes site assessment to determine the soil type and thermal conductivity, trenching or drilling for the ground loops, and installing the heat pump unit indoors. The complexity and cost of ground source installation can vary significantly depending on the land availability, soil conditions, and the type of ground loop configuration chosen.
Finding Qualified Installers in the US
To ensure a successful installation, it’s essential to find qualified and experienced installers. Homeowners can start by checking for certified professionals through organizations like the Air-Conditioning, Heating, Refrigeration Certification Board (ACHR) or the International Ground Source Heat Pump Association (IGSHPA). Additionally, seeking referrals from friends, family, or online reviews can help in identifying reliable installers.
By understanding the installation requirements and processes for both air source and ground source heat pumps, homeowners can better prepare for the installation and ensure that their system operates efficiently and effectively.
Initial Cost Comparison
The initial investment in a heat pump system can vary significantly based on the type chosen. Understanding these costs is crucial for homeowners looking to make an informed decision.
Air Source Heat Pump Costs
Air source heat pumps are generally less expensive to purchase upfront compared to ground source heat pumps. The cost of an air source heat pump can range from $3,000 to $15,000, depending on the capacity and features of the unit.
Ground Source Heat Pump Costs
Ground source heat pumps are more expensive to install, with costs ranging from $10,000 to $30,000 or more. The higher cost is largely due to the need for ground loop installation, which can be labor-intensive.
Installation Cost Factors
Several factors can affect the installation cost of both air source and ground source heat pumps. These include:
- The complexity of the installation
- The need for additional equipment such as buffers tanks or supplementary heating systems
- Local labor costs
| Cost Factor | Air Source Heat Pump | Ground Source Heat Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Unit Cost | $3,000 – $15,000 | $10,000 – $30,000 |
| Installation Cost | $1,000 – $5,000 | $5,000 – $15,000 |
| Total Cost | $4,000 – $20,000 | $15,000 – $45,000 |
Financing Options Available
To make heat pumps more accessible, various financing options are available. These include:
- Federal and state tax credits
- Utility company rebates
- Low-interest loans from financial institutions
Homeowners are advised to explore these options to help offset the initial cost of their chosen heat pump system.
Operating Costs and Efficiency
When evaluating heat pump options, operating costs and efficiency are key factors to consider. Both air source and ground source heat pumps offer unique benefits and challenges in terms of their efficiency and the costs associated with their operation.
Coefficient of Performance (COP)
The Coefficient of Performance (COP) is a crucial metric for measuring the efficiency of heat pumps. It represents the ratio of heating or cooling output to the electrical energy input. A higher COP indicates greater efficiency. For instance, a heat pump with a COP of 3.5 can produce 3.5 units of energy for every unit of electricity consumed.
Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER)
The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) is another important measure, particularly for cooling efficiency. It calculates the cooling output over a typical cooling season divided by the energy consumed. A higher SEER rating signifies better efficiency. Modern heat pumps often have SEER ratings between 13 and 22, with higher ratings indicating more efficient models.
Long-term Cost Analysis
Conducting a long-term cost analysis involves considering both the initial installation costs and the ongoing operating expenses. While air source heat pumps typically have lower upfront costs, ground source heat pumps can offer greater long-term savings due to their higher efficiency. The payback period for the higher initial cost of ground source systems can be significant, often ranging from 5 to 15 years.
Utility Bill Impacts
The impact of heat pumps on utility bills can be substantial. Efficient heat pumps can significantly reduce energy consumption, leading to lower bills. For example, a highly efficient air source heat pump can save homeowners up to 30% on their heating bills compared to traditional systems. Ground source heat pumps, with their higher COP, can offer even greater savings, especially in regions with extreme temperatures.
In conclusion, understanding the operating costs and efficiency of heat pumps is essential for making an informed decision. By considering metrics like COP and SEER, and analyzing long-term costs and utility bill impacts, homeowners can choose the most suitable heat pump for their needs.
Environmental Impact Assessment
With the rising awareness of climate change, assessing the environmental footprint of heat pumps is crucial. Both air source and ground source heat pumps offer eco-friendly alternatives to traditional heating systems, but their environmental impacts vary.
Carbon Footprint Comparison
The carbon footprint of heat pumps is largely determined by their source of electricity and efficiency. Air source heat pumps generally have a higher carbon footprint compared to ground source heat pumps due to their lower efficiency, especially in colder climates. However, advancements in technology are improving their efficiency.

Refrigerant Considerations
The refrigerants used in heat pumps have a significant environmental impact, particularly regarding their global warming potential (GWP). Modern heat pumps are moving towards using refrigerants with lower GWP, reducing their environmental impact.
Sustainability Factors
Sustainability is a key factor in the environmental impact assessment. Ground source heat pumps are often considered more sustainable due to their higher efficiency and lower operational carbon emissions. However, the initial installation impact, including land use and drilling, must be considered.
In conclusion, both air source and ground source heat pumps have their environmental pros and cons. Understanding these factors is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your sustainability goals.
Performance in Different US Climate Zones
The efficiency of heat pumps is heavily influenced by the climate zone in which they operate. Both air source and ground source heat pumps have unique performance characteristics that are affected by regional climate conditions.
Air Source Heat Pumps in Extreme Weather
Air source heat pumps are designed to operate in various weather conditions. However, their efficiency can be impacted by extreme temperatures.
- In cold climates, air source heat pumps may require supplemental heating.
- In hot climates, they can provide efficient cooling.
Ground Source Heat Pumps in Varying Conditions
Ground source heat pumps are generally more stable in their performance across different climates because they utilize the earth’s relatively constant temperature.
Key benefits include:
- Consistent efficiency in both cold and hot climates.
- Less dependence on air temperature fluctuations.
Regional Considerations: Northeast, Southeast, Midwest, and West
Different regions in the US have unique climate challenges that affect heat pump performance.
Cold Climate Performance
In colder regions like the Northeast and Midwest, ground source heat pumps tend to perform more consistently than air source heat pumps.
In hotter climates such as the Southeast and parts of the West, air source heat pumps can be effective for cooling, but their efficiency may decrease during peak summer months.
Understanding these regional considerations is crucial for selecting the right heat pump for your specific climate zone.
Space Requirements and Property Considerations
One of the key factors in choosing between an air source heat pump and a ground source heat pump is understanding their respective space requirements. Both types of heat pumps have different installation needs that can significantly impact your property.
Air Source Heat Pump Footprint
Air source heat pumps require less space compared to ground source heat pumps. They can be installed on a wall or placed on the ground outside your home. The unit’s compact design makes it suitable for urban settings where space is limited.
Ground Source Heat Pump Land Requirements
Ground source heat pumps, on the other hand, require more land because they involve burying pipes underground to absorb or dissipate heat. The amount of land needed can vary depending on the system’s size and the property’s soil characteristics.
Urban vs Rural Installation Challenges
The installation challenges for heat pumps differ significantly between urban and rural settings. In urban areas, space constraints and noise regulations can affect the installation of air source heat pumps. In contrast, rural areas may have more space available, but the terrain and soil conditions can pose challenges for ground source heat pumps.
| Heat Pump Type | Space Requirements | Installation Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Air Source | Compact; suitable for urban areas | Noise regulations; space constraints |
| Ground Source | More land required for underground pipes | Terrain and soil conditions; higher upfront cost |
Noise Levels and Aesthetic Impact
Noise levels and aesthetic appeal are crucial factors to consider when deciding between an air source heat pump and a ground source heat pump. The noise generated by these systems can significantly impact homeowner satisfaction and neighborhood harmony.
Air Source Heat Pump Noise Concerns
Air source heat pumps are known to produce more noise compared to ground source heat pumps, primarily due to their outdoor unit. The noise level can vary depending on the model and manufacturer, with some operating as quietly as 40 decibels.
Ground Source Heat Pump Noise Profile
Ground source heat pumps are generally quieter, as the majority of their components are buried underground. However, the indoor unit can still produce some noise, typically in the range of 20-30 decibels.
Neighborhood and HOA Considerations
When choosing a heat pump, it’s essential to consider neighborhood and HOA regulations regarding noise and aesthetics. A comparison of the noise levels and visual impact of different heat pumps is crucial.
| Heat Pump Type | Noise Level (Decibels) | Aesthetic Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Air Source | 40-60 | Outdoor unit visible |
| Ground Source | 20-30 | Minimal outdoor visibility |
Understanding these factors can help homeowners make an informed decision that meets their needs and complies with local regulations.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Understanding the maintenance needs and lifespan of heat pumps is crucial for homeowners considering air source or ground source options. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of these systems.
Air Source Heat Pump Maintenance
Air source heat pumps require regular checks to ensure they operate efficiently. This includes cleaning filters, checking for refrigerant leaks, and inspecting the outdoor unit for debris. Homeowners should schedule annual professional maintenance to prevent issues and maintain warranty validity.
Ground Source Heat Pump Maintenance
Ground source heat pumps also require regular maintenance, although the tasks differ slightly. They need annual inspections of the system’s electrical connections, filters, and refrigerant levels. The ground loop should be checked every 5-10 years to ensure it’s functioning correctly.
Expected Lifespan Comparison
Air source heat pumps typically have a lifespan of 15-20 years, while ground source heat pumps can last 20-25 years or more with proper maintenance. The longer lifespan of ground source systems can offset their higher initial costs over time.
Finding Service Providers
To maintain your heat pump, it’s crucial to find a qualified service provider. Look for professionals certified by organizations like NATE (North American Technician Excellence) or R-410A certified technicians. Check online reviews, ask for referrals, and verify licenses to ensure you’re hiring a reliable technician.

Federal and State Incentives in the US
The US government offers various incentives for homeowners who install heat pumps, promoting energy efficiency and reducing carbon footprint. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront costs of heat pump installations, making them more accessible to homeowners across the country.
Federal Tax Credits and Rebates
The federal government provides tax credits for homeowners who install qualifying heat pumps. For instance, the Residential Renewable Energy Tax Credit allows homeowners to claim a percentage of the installation costs on their tax returns. This credit can be substantial, helping to offset the initial investment.
- Eligible systems include air source and ground source heat pumps.
- The tax credit percentage may vary based on the year of installation.
State-Specific Incentive Programs
In addition to federal incentives, many states offer their own programs. For example, some states provide rebates or low-interest loans for heat pump installations. Homeowners should check with their state’s energy office to explore available programs.
Utility Company Programs
Many utility companies offer rebates and special rates for customers who install heat pumps. These programs can help reduce both the upfront costs and ongoing energy expenses.
How to Apply for Available Incentives
To apply for these incentives, homeowners typically need to submit an application along with proof of purchase and installation. It’s essential to keep detailed records and check the specific requirements for each program.
Real-World Performance Data
The actual performance of air source and ground source heat pumps can be understood through case studies and user experiences. By examining real-world data, homeowners can gain a clearer understanding of what to expect from these systems.
Case Studies: Air Source Heat Pumps
Several case studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of air source heat pumps in various climates. For instance, a study in the Northeast US showed that air source heat pumps maintained an efficiency of over 90% even in sub-zero temperatures.
Case Studies: Ground Source Heat Pumps
Ground source heat pumps have also been the subject of numerous case studies. A notable example from the Midwest highlighted a ground source heat pump system that achieved a Coefficient of Performance (COP) of 4.5, significantly reducing energy costs.
User Experiences and Satisfaction Rates
User experiences with both types of heat pumps have generally been positive. A survey of homeowners revealed that over 85% reported satisfaction with their heat pump systems, citing energy savings and comfort as primary benefits.
| Heat Pump Type | Average COP | User Satisfaction Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Air Source | 3.2 | 80% |
| Ground Source | 4.5 | 90% |
“Installing a ground source heat pump was one of the best decisions we made for our home. The energy savings are significant, and it’s so quiet and comfortable.” – Homeowner testimonial.
Future Developments in Heat Pump Technology
Innovations in heat pump technology are paving the way for more efficient and sustainable heating solutions. As research and development continue to advance, we can expect significant improvements in both air source and ground source heat pumps.
Emerging Air Source Heat Pump Innovations
Air source heat pumps are becoming increasingly sophisticated, with improved inverter technology allowing for more precise temperature control and reduced energy consumption. New models are also being designed to operate effectively in extreme weather conditions, expanding their applicability across different climates.
Advances in Ground Source Technology
Ground source heat pumps are benefiting from advancements in drilling technologies and heat exchange materials, making them more efficient and less invasive to install. These improvements are expected to reduce the upfront costs and increase the adoption rate of ground source systems.
Smart Home Integration Possibilities
The integration of heat pumps with smart home systems is set to revolutionize the way we manage our heating and cooling. With the ability to control heat pumps remotely and optimize their operation based on occupancy and preferences, homeowners can enjoy enhanced comfort and energy savings.
| Technology | Current Status | Future Development |
|---|---|---|
| Air Source Heat Pumps | High efficiency, variable speed | Improved performance in extreme weather |
| Ground Source Heat Pumps | Advanced drilling techniques | More efficient heat exchange materials |
| Smart Home Integration | Basic remote control | AI-driven optimization |
Which Heat Pump Is Right for Your Home?
With various heat pump technologies available, selecting the most suitable one for your home requires careful consideration of several factors. The choice between air source and ground source heat pumps depends on a multitude of factors including your property’s characteristics, your budget, and your long-term energy savings goals.
Decision Factors to Consider
When deciding on a heat pump, several key factors come into play. These include the initial cost, operating efficiency, and maintenance requirements. It’s essential to evaluate these factors in the context of your specific needs and circumstances.
Property-Specific Considerations
The type of heat pump that is right for you largely depends on your property. For instance, ground source heat pumps require sufficient land for the installation of ground loops, whereas air source heat pumps need less space but may be more visually obtrusive.
| Characteristics | Air Source Heat Pump | Ground Source Heat Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Space Requirements | Less land required | More land required for ground loops |
| Efficiency | Generally less efficient | More efficient, especially in extreme temperatures |
Budget Constraints vs Long-Term Savings
While air source heat pumps typically have a lower upfront cost, ground source heat pumps can offer significant long-term savings due to their higher efficiency. It’s crucial to balance your initial budget constraints with the potential for future savings.
Consulting with HVAC Professionals
Given the complexity of choosing the right heat pump, consulting with HVAC professionals is highly recommended. They can provide personalized advice based on your home’s specific needs and your budget.
Conclusion
Choosing between an air source heat pump and a ground source heat pump depends on several key factors, including your home’s specific needs, budget, and local climate. Throughout this comparison, we’ve explored the core differences, installation requirements, operating costs, and environmental impacts of both systems.
Air source heat pumps offer a more straightforward and cost-effective installation process, making them an attractive option for many homeowners. On the other hand, ground source heat pumps provide higher efficiency and longer lifespan, albeit with a more complex and initially costly installation.
Ultimately, the decision comes down to weighing the upfront costs against long-term savings and considering your property’s unique conditions. By carefully evaluating these factors and consulting with HVAC professionals, you can make an informed decision that best suits your needs.
In the end, selecting the right heat pump can significantly enhance your home’s comfort and energy efficiency, making it a worthwhile investment for the future.
FAQ
What is the main difference between air source and ground source heat pumps?
The primary difference lies in their heat source; air source heat pumps extract heat from the air, while ground source heat pumps extract heat from the ground.
Are air source heat pumps effective in cold climates?
Yes, air source heat pumps can be effective in cold climates, but their efficiency may decrease as temperatures drop. Modern models, such as those from Carrier or Lennox, are designed to operate efficiently even in colder temperatures.
How much space is required for a ground source heat pump installation?
The space required for a ground source heat pump depends on the type of system (horizontal or vertical) and the property’s soil conditions. Generally, a significant amount of land is needed for horizontal installations.
What are the typical costs associated with installing an air source heat pump?
The cost of installing an air source heat pump can vary widely depending on factors like the unit’s capacity, model, and installation complexity. On average, homeowners can expect to pay between $3,000 to $7,000 for a high-efficiency unit from brands like Trane or Rheem.
Are there any incentives available for heat pump installations in the US?
Yes, there are federal and state incentives available, including tax credits and rebates, to encourage the adoption of energy-efficient heat pumps. Homeowners can also explore utility company programs that offer additional savings.
How do I choose between an air source and ground source heat pump for my home?
The choice between an air source and ground source heat pump depends on several factors, including your property’s size and layout, local climate, budget, and personal preferences. Consulting with HVAC professionals can help you make an informed decision.
What is the expected lifespan of a heat pump?
The average lifespan of a heat pump is around 15 to 20 years, depending on the type, quality, and maintenance. Regular maintenance can help extend the lifespan of your heat pump.
Can heat pumps provide both heating and cooling?
Yes, heat pumps are capable of providing both heating and cooling by reversing the flow of refrigerant. This makes them a versatile solution for year-round comfort.
How do I maintain my heat pump to ensure optimal performance?
Regular maintenance tasks include cleaning filters, inspecting coils, and checking refrigerant levels. It’s also recommended to schedule annual professional maintenance to ensure your heat pump operates efficiently and effectively.


Leave A Comment